Published on: September 23, 2025 | By: Nagendra Dhimal | Category: NEB Exam Solutions
Are you searching for the Class 12 Re-Exam Accountancy Question Solution 2082? If you’ve just appeared for the NEB Grade 12 Supplementary Accountancy Exam (Subcode: 1041’A’) or are preparing for future revisions, this comprehensive guide is your one-stop resource. As a leading education blog in Nepal, NagendraDhimal.com.np brings you detailed, step-by-step solutions to all sections of the NEB Class 12 Accountancy Re-Exam 2082 paper.
Whether you’re a student aiming to understand the marking scheme, teachers verifying answers, or parents helping their kids, we’ve covered everything—from Group A concepts to numerical problems in Groups B-E, including EOQ, share journal entries, financial statements, cash flows, and cost sheets. Our solutions align with the official NEB guidelines and NFRS, ensuring accuracy and full marks potential.
Quick Links to Sections:
- Group A: Very Short Answers
- Group B: Short Answers
- Group C: Long Answers – Financial Statements
- Related Posts
Meta Description: Get the complete Class 12 Re-Exam Accountancy Question Solution 2082 for NEB Grade 12 Supplementary Exam. Detailed answers to EOQ, journal entries, financial statements, cash flows, and cost sheets. Download PDF for free at NagendraDhimal.com.np.
Keywords: class 12 re exam accountancy question solution 2082, neb grade 12 accountancy supplementary exam 2082 answers, class 12 account re-exam solutions 2082, neb accountancy paper solution 2082, grade 12 accountancy model questions 2082
Why This Class 12 Accountancy Re-Exam 2082 Solution Guide Matters
The NEB Grade 12 Accountancy Supplementary Exam 2082 (conducted Bhadra 28-29, 2082) focused on practical application of concepts like cost accounting, company accounts, and NFRS reporting. With 75 marks and 3 hours duration, it tested theory (Group A), calculations (EOQ, shares), and statements (P/L, BS, cash flow). Challenges included pro-rata allotments and FIFO inventory.
Our Class 12 Re-Exam Accountancy Question Solution 2082 includes workings for numericals and explanations for theory, optimized for 90%+ scores. Updated September 23, 2025—subscribe for free PDFs!

Group A: Very Short Answer Questions [11×1=11]

- Write the meaning of company. A company is an artificial person created by law, having a separate legal entity, perpetual succession, and limited liability, formed for profit-making through shares.
- What is ordinary share? Ordinary shares represent ownership in a company, entitling holders to dividends after preference shareholders and voting rights, but with higher risk.
- State the meaning of fixed assets. Fixed assets are long-term tangible or intangible resources used in business operations, like machinery or buildings, not intended for sale.
- Define cost accounting. Cost accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and analyzing costs to control and reduce them, aiding management decisions.
- Classify the overhead based on function. Production overhead (factory), administrative overhead (office), selling & distribution overhead.
- Write the meaning of direct material cost. Direct material cost is the expense of raw materials directly traceable to the production of specific goods, like wood in furniture.
- What is job card? A job card is a document recording costs (materials, labor, overhead) for a specific job or order in job costing systems.
- What is account masters in computer? Account masters are database files storing details of ledger accounts (e.g., codes, names, balances) in computerized accounting software like Tally.
- Prepare adjustment entry for provision for income tax Rs.40,000. Journal Entry: Profit & Loss A/c Dr. 40,000 To Provision for Income Tax A/c 40,000 (For creating provision for income tax)
Pro Tip: Keep answers concise (20-30 words) for full marks. Download Group A notes PDF here.
Group B: Short Answer Questions [5×8=40]


- Calculate EOQ from given data. (Annual requirement: 80,000 units; Ordering cost: Rs.10/order; Carrying cost: Rs.40/unit/year) EOQ = √(2 × Annual Demand × Ordering Cost / Carrying Cost) = √(2 × 80,000 × 10 / 40) = √40,000 = 200 units. (This minimizes total inventory costs.)
- Pass journal entries for share issue. (20,000 shares Rs.100 at 10% discount; Application Rs.30, Allotment Rs.30, First & Final Call Rs.30; Applications 28,000 shares; Allotment details provided; Excess adjusted; All received except 800 shares calls unpaid.) Journal Entries: (i) Bank A/c Dr. 8,40,000 To Share Application A/c 8,40,000 (Application money on 28,000 shares @ Rs.30)
(ii) Share Application A/c Dr. 8,40,000 To Share Capital A/c 6,00,000 To Share Allotment A/c 2,40,000 (Transfer to capital on 20,000 shares; excess to allotment)
(iii) Share Allotment A/c Dr. 6,00,000 To Share Capital A/c 6,00,000 (Allotment due @ Rs.30)
Bank A/c Dr. 3,60,000 To Share Allotment A/c 3,60,000 (Cash received after adjustment)
(iv) Share First & Final Call A/c Dr. 6,00,000 To Share Capital A/c 6,00,000 (Calls due @ Rs.30)
Bank A/c Dr. 5,76,000 To Share First & Final Call A/c 5,76,000 (Received except Rs.24,000 on 800 shares)
(v) Share First & Final Call A/c Dr. 24,000 Share Capital A/c Dr. 72,000 (800 × Rs.90 issue price) To Forfeited Shares A/c 72,000 (Forfeiture of 800 shares; assume at issue price Rs.90)
- Calculate cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO (periodic system). (From given purchases/sales data; assume standard table: Opening 20,000 @ Rs.24; Purchases: 40,000 @ Rs.25, 30,000 @ Rs.26; Sales 70,000 units.) FIFO Calculation: Available: 20,000 @24 = 4,80,000; 40,000 @25 = 10,00,000; 30,000 @26 = 7,80,000; Total units 90,000; Cost Rs.22,60,000. COGS (first 70,000): 20,000@24 + 40,000@25 + 10,000@26 = 4,80,000 + 10,00,000 + 2,60,000 = 17,40,000. Ending Inventory (20,000@26) = 5,20,000.
- Calculate total wages of workers. (Standard time 4 hrs/unit; Wages Rs.400/unit; 200 hrs worked/month.) Units produced = 200 / 4 = 50 units. Total wages = 50 × 400 = Rs.20,000.
- Prepare Cost Reconciliation Statement. (Net profit Rs.40,000; Interest Rs.5,000; Overval stock Rs.15,000; Under office OH Rs.10,000.) Cost Reconciliation Statement: Financial Profit 40,000
- Items credited in financial but not cost: Interest 5,000
- Items debited in financial but not cost: Overvaluation of stock (15,000)
- Items credited in cost but not financial: Under-rec. office OH 10,000 Cost Profit: Rs.40,000.
Related Read: NEB Grade 12 Cost Accounting Notes 2082
Group C: Long Answer Questions – Financial Statements [3×8=24]
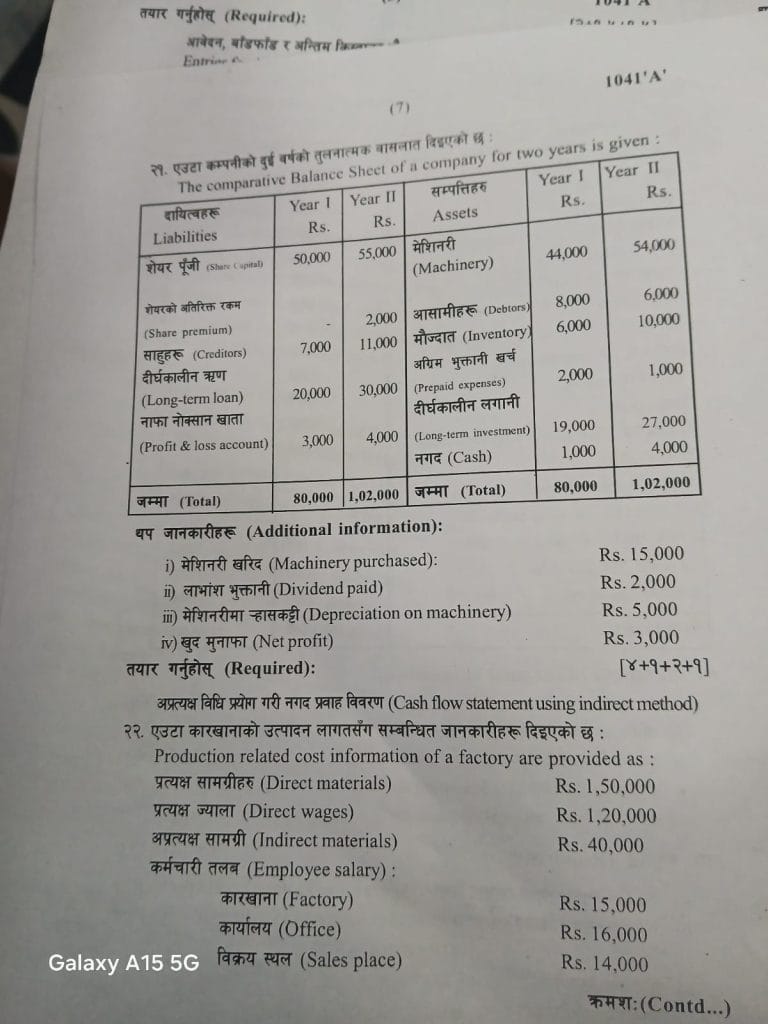
- Define computerized accounting system. Explain usages of computer system in accounting. Computerized accounting uses software (e.g., Tally) to automate recording, processing, and reporting. Usages: (i) Accuracy & speed in ledger posting; (ii) Automated trial balance & financial statements; (iii) Error detection via reconciliation; (iv) MIS reports for decisions; (v) Data security & backups; (vi) Integration with GST/VAT compliance.

